We ❤️ Open Source
A community education resource
Demystifying external data as a service
Use these tactics to effectively manage external data sources for real-time decision-making.

Utilizing external data in real-time has become crucial in today’s evolving world of financial institutions and in making decisions in time. Whether it’s evaluating a client’s financial status or mitigating fraud risks, tapping into external data is vital. Yet smoothly incorporating, processing, and analyzing this data in real-time presents challenges. This article explores the approaches to managing the complexities of the external data orchestration layer that plays an important role in integrating and processing external data in financial institutions. These approaches and methods are based on knowledge gathered over time and help improve the efficiency, reliability, and scalability of handling external data.
Five key takeaways from this article:
- Role of external data in real-time financial decisions: External data is indispensable for financial institutions, helping them verify identities, prevent fraud, and manage risks. This data allows institutions to make well-informed decisions by drawing from a variety of reliable sources.
- Challenges in real-time data use: Managing real-time external data comes with challenges such as latency, different data formats, system reliability, scalability, and data privacy concerns. Addressing these challenges requires a blend of technical skills, smart architectural planning, and effective operational strategies to build a robust and scalable data orchestration system.
- Strategies for efficient data handling: To tackle these challenges, financial institutions use methods like parallel processing, caching, automated error handling, dynamic scaling, and data quality monitoring. These strategies enhance the efficiency and reliability of data handling, leading to better decision-making.
- Insights from a case study: A detailed case study shows the benefits of separating the orchestration layer from the external data processing layer for independent scaling and system resilience. It also highlights the advantages of centralized storage for caching, dynamic configuration of data sources, real-time streaming for archival needs, and robust monitoring systems to ensure smooth operations and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Best practices for architecture and operations: Financial institutions can improve their data orchestration processes by developing efficient orchestration logic, implementing automatic schema validation, ensuring fault tolerance, securely handling sensitive data, and maintaining scalability. Adopting these best practices helps organizations optimize their data orchestration systems, leading to better decision-making, increased efficiency, and greater resilience in the dynamic financial industry.
Overview and significance of external data in decision-making
External data is an integral part of financial institutions on identity verification, fraud prevention, and managing risks. By tapping into external data reports, financial institutions can detect fraudulent activities, assess creditworthiness, and mitigate financial risks.
Identity verification
One of the primary uses of external data is identity verification. Whether it’s verifying individual customers or small businesses, having reliable data to confirm identities is essential. External data sources leverage pre-existing government-issued IDs, utility bills, and official documents in this verification process. By referencing information from these sources, financial institutions can ensure that they are engaging with genuine individuals or businesses, thus reducing the chances of identity theft and fraud.
Fraud prevention
Utilizing data is also crucial for preventing fraud while making financial decisions in real time. By conducting checks on data points, institutions can flag potential warning signs and suspicious activities. Some critical areas where external data comes into play for fraud prevention include:
- Address verification: Confirming individual or business addresses can help to identify activities like identity theft or account takeover.
- Phone number verification: Validating phone numbers helps in ensuring that customers can be reached for verification purposes while minimizing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
- Email address verification: Checking email addresses is essential to confirm users’ identities and avoid unauthorized access to accounts or access to data. By verifying the email address, financial organizations can protect their client’s assets and uphold the integrity of their services.
Risk management
In today’s landscape, effective risk management is one of the most important parts of the success of financial institutions. External data plays a role in evaluating and handling risks related to lending and credit decisions. Some key elements in risk management include:
- Credit report analysis: Financial institutions use data from credit agencies to assess the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses. Through the analysis of credit reports, financial institutions can gauge the likelihood of default and make informed choices regarding extending credit.
- Alternative data sources: Apart from credit reports, financial institutions also take into consideration alternative data sources like utility payments and rent information. These sources offer insights into an individual’s habits and support in evaluating their creditworthiness, particularly for individuals with limited credit histories.
By integrating data into their risk management procedures, financial institutions can enhance the accuracy of their assessments and reduce potential financial losses.
Orchestrating external data in real time: Challenges
Managing real-time external data presents challenges, such as latency, different data formats, system reliability, adaptability, security, privacy concerns, and operational excellence. These challenges involve efficiently handling data, ensuring data consistency across sources, maintaining system resilience in case of failures, and expanding systems to meet growing needs while addressing privacy and security issues.
- Latency: Orchestrating real-time data involves processing data fast while minimizing delays between processing and making a decision for the end user.
- Data formats: Ensuring the accuracy, quality, and integrity of various data types is complex.
- System reliability: Real-time data systems are vulnerable to failures like network outages, hardware malfunctions, or software glitches that can disrupt processing or lead to data loss.
- Scalability: Adapting real-time systems to handle increasing amounts of data and user demands while maintaining performance is a challenge.
- Data privacy and security: Processing external data introduces concerns about privacy risks, security breaches, and maintaining compliance requirements.
- Operational monitoring and management: To effectively oversee and control real-time data orchestration systems, it is essential to understand the performance and resource utilization.
Overcoming these obstacles involves a blend of technical knowledge, architectural planning, and operational strategies to build a robust and scalable real-time data orchestration system.
Strategies for efficient external data orchestration
To manage the complexities and challenges, the below strategies can be employed:
- Parallel processing: retrieving data sources simultaneously is essential to make decisions early in the process. This reduces delays and ensures timely access to critical data.
- Caching: By incorporating caching mechanisms, organizations can store used data locally for reuse when permissible by regulations or consent. This minimizes reliance on external sources and enhances overall performance.
- Automated exception handling: These mechanisms enable systems to retry accessing data sources or switch to alternative sources in case of failures or unavailability.
- Dynamic scaling: The ability to dynamically scale allows organizations to efficiently adjust to changing data volumes and user demands. By utilizing data and future growth projections, intelligent scaling mechanisms can be implemented to manage peak loads and spikes in data traffic effectively.
- Data quality monitoring: Integrating robust monitoring systems with data quality monitoring is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of data processing workflows. Early detection of anomalies helps address issues promptly, preventing disruptions in the workflow.
- Data standardization: Implementing practices for data standardization and extracting data from sources helps organizations achieve a flexible connection. This adaptability allows organizations to smoothly transition between data sources as per changing business needs and requirements.
Techniques like running processes simultaneously, storing data temporarily, automatically handling exceptions, adjusting scale dynamically monitoring data quality, and ensuring standardization of data all play roles in streamlining data organization procedures. By embracing these approaches, organizations can improve effectiveness, dependability, and scalability in handling external data sources, ultimately leading to decision-making results and successful business outcomes.
Case study: Design
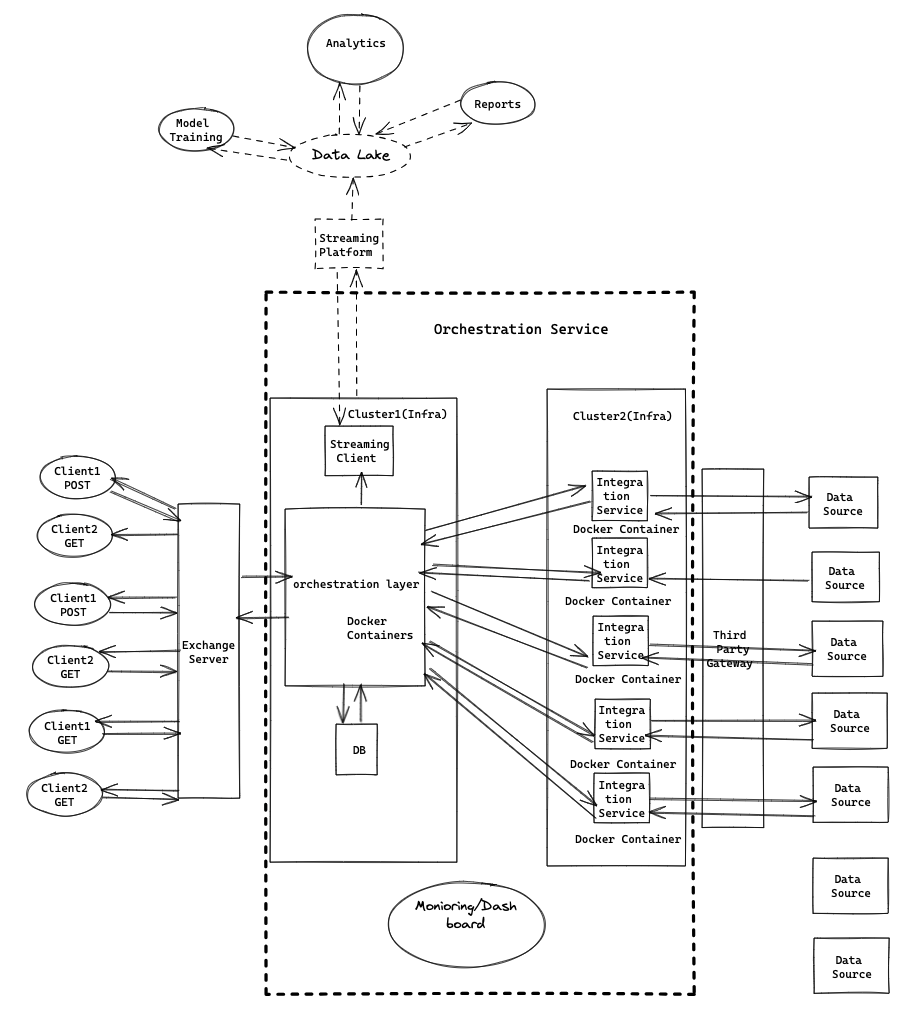
Note: The above diagram is used only for illustration purposes
The orchestration layer and the external data processing layer, often referred to as the Integration Service, are intentionally kept separate to ensure independent scaling in each layer according to system requirements. By separating these layers, organizations can guarantee performance and resource usage during peak demand or heavy workloads.
Moreover, all external reports are stored in a database, for caching purposes to meet the regulatory standards. This centralized storage method enables access to frequently used reports but also ensures compliance with data retention regulations.
The orchestration layer is configured dynamically to accommodate combinations of requested data sources. This configuration-driven approach enhances flexibility and adaptability, enabling the system to integrate new data sources based on evolving business needs or user demands.
Real-time streaming capabilities are utilized to store data in a data lake for archival and analytical requirements. This ensures valuable data is preserved for analysis, allowing organizations to extract actionable insights and make informed decisions based on historical data.
A strong monitoring system is set up to keep an eye on both the business functions and the health of the system infrastructure continuously. This monitoring assistance helps companies to detect and deal with any issues or abnormalities, ensuring smooth system operations and minimizing downtime or interruptions.
Furthermore, operational and archival data are kept separate for efficient storage costs and adherence to regulatory guidelines. This separation of data facilitates organizations in managing resources while also meeting data governance and regulatory standards. To improve the effectiveness of external data orchestration, various additional strategies can be put into action:
- Efficient orchestration logic: Developing orchestration logic, implementing caching mechanisms, and applying scaling policies are key to reducing delays and ensuring prompt retrieval of response data. By optimizing these areas, organizations can improve the performance of their data orchestration processes.
- Automatic schema validation and data quality configuration: Utilizing automatic schema validation and configuration-based data quality management can help maintain data accuracy and integrity across data sources. By validating schemas and setting data quality parameters, organizations can streamline data processing workflows. Minimize the chances of errors or inconsistencies.
- Fault tolerance: Creating orchestration components with a limited impact radius and ensuring their ability to respond effectively in case of failures is crucial for maintaining system reliability. By integrating fault tolerance architectures and mechanisms, organizations can minimize the effects of failures and increase the availability of their data orchestration systems.
- Sensitive data handling: Implementing capabilities to scan and mask or eliminate information before sharing it within the ecosystem is vital for safeguarding data privacy and adhering to standards. Through data masking and anonymization methods, organizations can protect details and reduce the risks associated with potential data breaches.
- Scalability: Adjusting components to scale efficiently in response to changing demands is essential for managing evolving data processing needs.
Conclusion
In summary, effectively managing external data sources is vital for making informed decisions in the fast-moving realm of financial institutions. External data plays an important role in verifying identities, preventing fraud, and managing risks, allowing institutions to evaluate customers’ financial health and mitigate risks. However, seamlessly integrating and processing external data poses challenges, including performance, diverse data types, fault tolerance, scalability concerns, privacy/security considerations, and operational management complexities.
To tackle these obstacles, organizations utilize a range of tactics including parallel processing methods, caching mechanisms, automated error-handling processes, dynamic scaling approaches, data quality checks, and data standardization. These tactics bolster efficiency levels while ensuring reliability and scalability in handling data sources, ultimately leading to better decision-making outcomes and business achievements.
Moreover, the architectural design focused on data processing emphasizes the importance of separating the orchestration layer from the external data processing layer to facilitate seamless scaling operations. Additionally, keeping records in a database for caching purposes and adhering to regulatory guidelines ensure swift access to frequently used reports while staying compliant with regulatory requirements.
Overall, by implementing robust monitoring systems, harnessing real-time streaming capabilities, and distinguishing operational stores from archival store facilities, organizations can enhance performance levels significantly while promoting scalability and compliance when managing external data sources. This smart method of handling data and organizing enables institutions to navigate the intricacies of today’s financial environments, driving greater success and resilience in the constantly changing finance industry.
The opinions expressed on this website are those of each author, not of the author's employer or All Things Open/We Love Open Source.
